How to Make Lab Grown Diamonds
The Mintly Team
December 14, 2023Diamonds have long been revered for their brilliance and rarity, traditionally sourced from the depths of the earth. However, advancements in technology have paved the way for an extraordinary alternative: lab-grown diamonds. These diamonds are not fakes or simulants; they boast the same physical and chemical properties as their mined counterparts. Here’s an insight into the fascinating process of creating diamonds in a laboratory setting.
Understanding Lab Grown Diamonds
Lab grown diamonds is also known as synthetic or cultured diamonds. Using advance technological process, genuine diamonds are produced in controlled laboratory environments. They replicate the conditions under which natural diamonds form over millions of years within the Earth’s crust.
There are two primary methods used to create lab grown diamonds. High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The HPHT process mimics the natural formation of diamonds by subjecting a small diamond seed to high temperatures and pressures. This environment dissolves carbon into a diamond lattice, growing it layer by layer. Alternatively, the CVD method involves breaking down gases in a vacuum chamber to deposit carbon atom-by-atom onto a substrate, where it crystallizes into diamond.
Lab grown diamonds possess the same physical, chemical, and optical properties as mined diamonds, making them indistinguishable to the naked eye. They offer several advantages, such as being more environmentally friendly due to reduced mining impact, and potentially being more ethical, as they bypass issues related to conflict diamonds. Additionally, they are often more affordable than their natural counterparts.
Still, it’s important to note that while lab grown diamonds are real diamonds with identical properties to mined ones, they may carry different sentimental and investment values. The choice between a lab-grown and a mined diamond ultimately depends on personal preference, values, and consideration of their respective impacts.
The Creation Process of Lab Grown Diamonds
The journey of creating a lab-grown diamond begins with a seed. The seed is a thin slice of diamond which is useful as a foundation upon which the new diamond will grow. There are two primary methods used to grow diamonds in a laboratory. These are High Pressure-High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
High Pressure-High Temperature (HPHT)
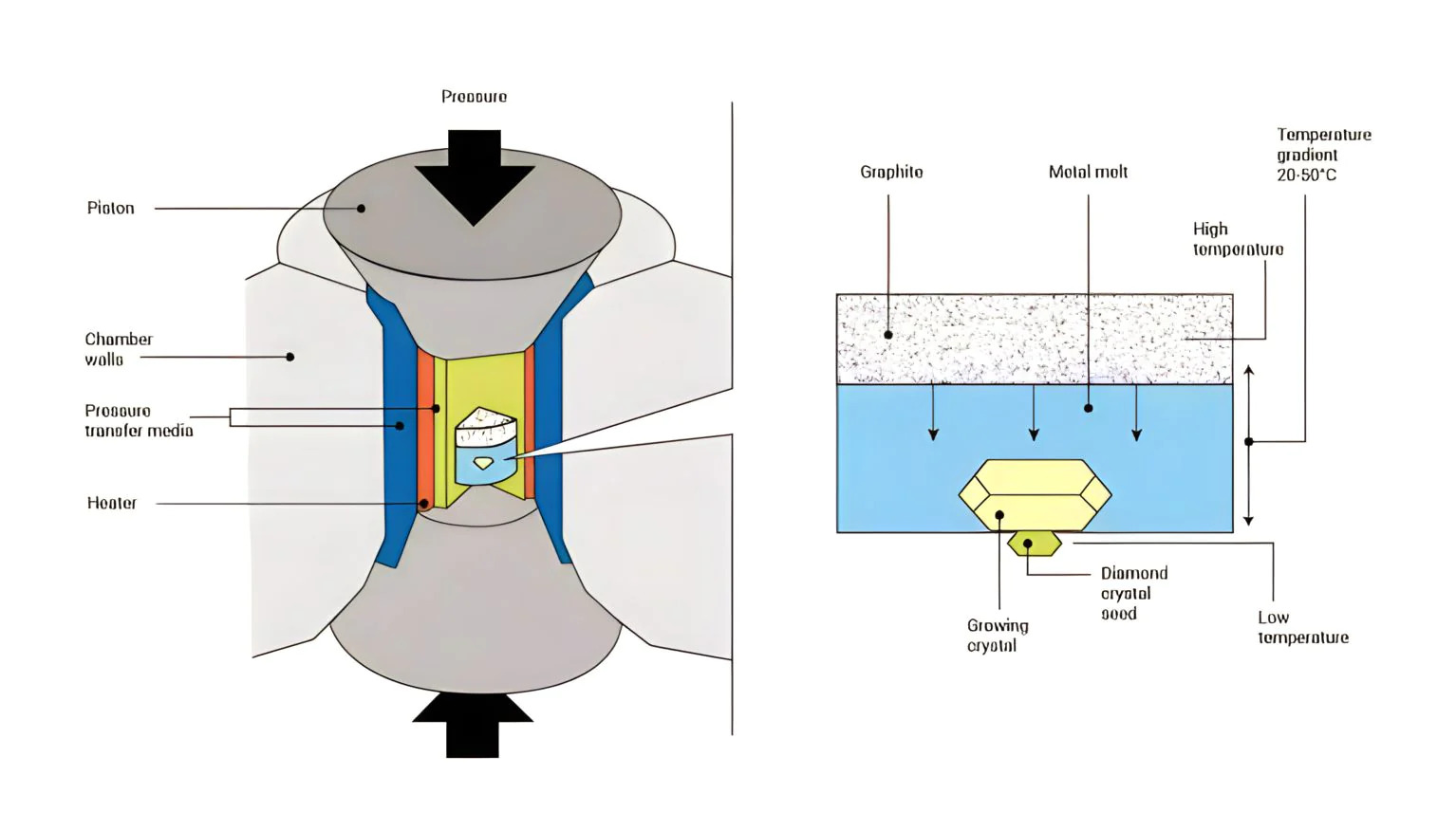
High Pressure-High Temperature (HPHT) is a significant method for creating lab-grown diamonds, which replicates the natural process of diamond formation beneath the Earth’s crust. At the core of this technology lies the simulation of the conditions that occur over a billion years underground, where carbon crystallizes into diamonds due to intense heat and pressure.
The HPHT process begins with a small diamond seed placed into carbon, the element required for diamond crystallization. You heat this assembly to conditions of extreme pressure. This is typically between 5 to 6 GPa, and temperatures ranging around 1400 to 1600 degrees Celsius. These parameters are sustained within a specialized press, often a belt, cubic, or a split-sphere (BARS). These are the three main types used to produce the necessary environment for diamond growth.
Under these conditions, the carbon melts and starts to form a diamond around the initial seed. The seed acts as a template for the atomic structure, ensuring that the lab-grown diamond replicates the properties of a natural gem. The time taken for growth can range from several hours to days, depending on the desired size and quality of the diamond.
Advantage of HPHT Diamonds
One of the key advantages of HPHT diamonds is their quality. They often match or even surpass mined diamonds in terms of clarity and color. Additionally, HPHT can enhance or alter the color of diamonds. This is producing rare and sought after hues which is less commonly found in nature.
HPHT diamonds are also an ethical and sustainable alternative to mined diamonds since they reduce the need for disruptive mining practices. They offer a more environmentally friendly option with a significantly smaller carbon footprint.
The HPHT method is revolutionizing the gem industry by providing an eco-friendly solution. This is happening without compromising on the brilliance or quality that diamonds is famous for. This process is. making them an increasingly popular choice among consumers looking for responsible luxury.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a cutting-edge technology widely utilized in the creation of lab-grown diamonds. This sophisticated process replicates the natural growth environment of diamonds, which traditionally occurs beneath the Earth’s surface under extreme heat and pressure. The CVD method, however, requires less onerous conditions, making it an increasingly popular technique for diamond synthesis.
The process begins by placing a thin slice of diamond, known as a seed crystal, inside a vacuum chamber. The chamber is then filled with a carbon-rich gas mixture, typically methane and hydrogen. Once the environment is prepared, the gases are energized using microwaves or other sources of energy to create a plasma. This high-energy plasma breaks down the gas molecules, releasing carbon atoms.
These free carbon atoms start to precipitate onto the cooler diamond seed in layers, adhering to its crystalline structure. Over several weeks, the carbon atoms continue to deposit, and the diamond grows atom by atom, creating a three-dimensional gem-quality stone.
CVD diamonds possess qualities comparable to those found in naturally occurring diamonds. They are identical in chemical composition, physical properties, and optical characteristics, rendering them indistinguishable without specialized equipment. The controlled conditions of the CVD process allow for the production of diamonds with fewer defects and impurities than those commonly found in nature.
Moreover, CVD diamonds is famous for growing in a laboratory set up. This type of production avoids the environmental degradation and ethical concerns. Most of these hazards occur due to traditional mining practices. This aspect has made CVD diamonds an appealing alternative for consumers seeking sustainable and responsible choices in fine jewelry.
The versatility of the CVD method also enables the development of diamonds for industrial applications. The ability to engineer diamonds with specific properties is invaluable for various uses in electronics, cutting tools, and high-performance optics.
The Benefits of Lab Grown Diamonds
Lab grown diamonds offer a multitude of benefits, serving as an ethical, sustainable, and economical alternative to mined stones. These diamonds are identical to their natural counterparts in chemical composition, physical properties, and visual appearance. In spite of this, they are created above ground in controlled environments.
One of the most significant advantages is their minimal environmental impact. Traditional diamond mining is resource-intensive, often leading to significant ecological disruption, habitat destruction, and soil erosion. In contrast, lab-grown diamonds require significantly less land and water, reducing their environmental footprint and preserving natural landscapes.
Ethically, lab grown diamonds present a clear conscience choice. They circumvent issues associated with conflict diamonds, such as funding violence and exploiting workers. Lab-created diamonds ensure traceability and transparency. There by they offering consumers peace of mind that their purchase does not contribute to human rights abuses.
Economically, lab grown diamonds are more accessible due to their lower price point. They can cost up to 30% less than mined diamonds, making luxury more attainable. This cost-effectiveness also allows buyers to purchase larger or higher quality stones within the same budget.
Innovation in the creation process continues to advance, making lab-grown diamonds increasingly popular among consumers seeking responsible luxury. As technology progresses, these diamonds are likely to become even more indistinguishable from mined ones, further solidifying their position in the market.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their growing popularity and potential for sustainability, several challenges and considerations persist.
Market Acceptance and Value Perception: Consumer acceptance remains a significant challenge. Traditionalists often prefer natural diamonds for their perceived rarity and natural origin, which are deeply intertwined with their sense of value and emotional significance. Lab-grown diamonds must overcome this bias to gain a stronger foothold in the market.
Regulation and Disclosure: Ensuring that lab-grown diamonds are properly disclosed and differentiated from natural diamonds is crucial to maintaining consumer trust. The diamond industry must rigorously implement regulations to prevent misrepresentation and confusion among buyers.
Production Costs and Energy Consumption: While lab-grown diamonds are touted as an eco-friendly option, the energy-intensive production process presents a paradox. The reliance on substantial amounts of electricity, often derived from non-renewable sources, raises questions about their environmental impact.
Technological Advancements: The quality and size of lab-grown diamonds have historically limitation in terms of technological constraints. Constant research and development are required to enhance the efficiency and capabilities of diamond-growing methods, which necessitate significant investment.
Economic Impact: The rise of lab-grown diamonds could destabilize traditional mining economies that depend on natural diamond extraction. This shift could have profound socioeconomic implications for countries where diamond mining is a critical industry.
Ethical Considerations: Lab grown diamonds offer a solution to the ethical issues associated with diamond mining. You can expect frequently coming Issues such as labor rights violations and conflict funding. They also create new ethical dilemmas about value, authenticity, and tradition in the jewellery industry.
Conclusion
Lab-grown diamonds represent a remarkable fusion of science and artistry, providing a sustainable and ethical alternative to mined diamonds. As technology continues to advance, we can expect these gems to become increasingly prevalent in jewelry collections around the world.
Are you looking at lab grown diamonds for their environmental benefits, ethical implications?. Or simply the beauty and affordability of LGD?. It’s clear that these marvels of modern science are here to stay. With their indistinguishable characteristics from mined diamonds, lab-grown varieties offer all the sparkle with fewer compromises.
All Tags
Loading...
Loading...